Here’s why eating garlic and onions can prevent hypertension and diabetes
04/16/2021 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez

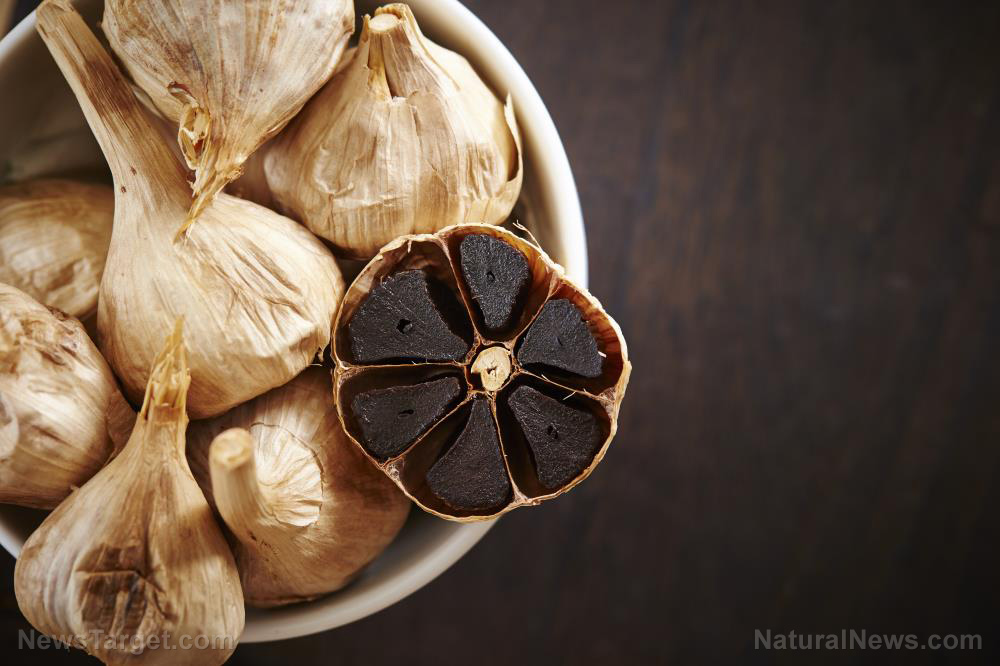
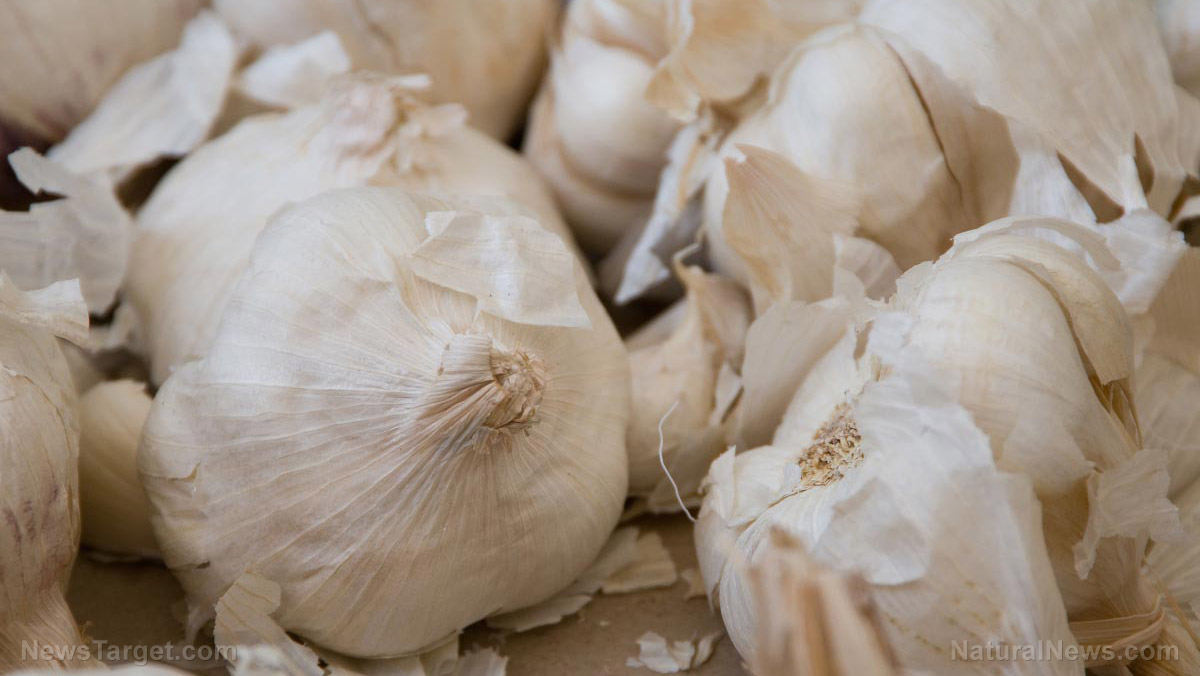
Alliums are disease-fighting vegetables widely used as everyday food and traditional medicines. This incredible family of edible medicinal plants is composed of garlic, white and purple onions, leeks, chives, scallions and shallots. According to studies, alliums contain unique compounds called organosulfur compounds and natural antioxidants called polyphenols that are responsible for their disease-fighting activities.
In a recent study, researchers at the Federal University of Technology in Nigeria investigated the benefits of eating garlic, white onion and purple onion against serious conditions like diabetes and hypertension. They confirmed these by looking at how extracts from the three alliums affect the activity of diabetes-related enzymes, such as a-amylase and a-glucosidase, and the hypertension-related enzyme, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE).
The researchers reported their findings in an article published in the Journal of Dietary Supplements.
Garlic, white onion and purple onion show antioxidant, antidiabetic and antihypertensive properties
Garlic and onions are spices commonly used in cooking. They also serve as ingredients in several traditional delicacies in Nigeria that are known to contain plenty of polyphenols. To assess the beneficial properties of garlic, white onion and purple onion, the researchers first obtained extracts from each and assessed their inhibitory effects on certain enzymes. They also conducted assays to determine the antioxidant capacities of the extracts.
ACE is the enzyme responsible for converting angiotensin I into angiotensin II, the hormone that increases blood pressure, as well as body water and sodium content. Angiotensin II elevates blood pressure by constricting the blood vessels; hence, chemicals that can inhibit the activity of ACE, which is responsible for the production of angiotensin II, are used for the treatment of hypertension. (Related: Meet the “two-day cure” plant: An African medicinal plant that can naturally lower blood pressure.)
a-Amylase is the enzyme that breaks down starch and glycogen into glucose and maltose (two glucose molecules bound together). In humans, this enzyme is produced by the salivary glands and the pancreas. a-Glucosidase, on the other hand, is responsible for breaking down carbohydrates in the small intestine and facilitating the absorption of glucose. Inhibiting the activity of this enzyme is one of the strategies currently used to prevent the rise of blood sugar levels following a carbohydrate-filled meal.
The researchers reported that the garlic, purple onion and white onion extracts inhibited the activities of ACE, a-amylase and a-glucosidase in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. At a half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 0.59 mg/mL, the purple onion extract exhibited a higher inhibitory effect on ACE than the white onion extract (IC50 = 0.66 mg/mL) and the garlic (IC50 = 0.96 mg/mL) extract.
Meanwhile, the white onion extract showed a significantly stronger inhibitory effect on a-amylase at an IC50 of 3.93 mg/mL than the garlic extract (IC50 = 8.19 mg/mL) and the purple onion (IC50 = 8.27 mg/mL) extract. The garlic extract, on the other hand, showed a similar inhibitory effect (IC50 = 4.50 mg/mL) on a-glucosidase as the white and purple onion extracts. All three extracts also showed dose-dependent free radical scavenging activity and reducing power in the antioxidant assays.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that garlic, white onion and purple onion can be used to treat or prevent diabetes and hypertension, thanks to their ability to inhibit ACE, a-amylase and a-glucosidase activity, as well as lipid peroxidation in the pancreas and the heart.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, anti-diabetes, antihypertensive, antioxidant, food cures, food is medicine, functional foods, garlic, heart health, herbal medicine, Herbs, natural cures, natural medicine, onions, remedies, research, Spices
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
FoodIsMedicine.com is a fact-based public education website published by Food Is Medicine Features, LLC.
All content copyright © 2018 by Food Is Medicine Features, LLC.
Contact Us with Tips or Corrections
All trademarks, registered trademarks and servicemarks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.