Nobody is talking about gout: Here’s why
01/06/2020 / By Grace Olson
In the U.S., over 83 million people suffer from gout – that’s one in 25 people. While the painful condition is becoming more common each year, not everyone is familiar with it, and not everyone who suffers from it seeks help and treatment. This is a problem not only for those who have gout but to healthcare professionals as well.
Read on to learn more about gout, how it occurs, its history and how to prevent it.
A guide to gout – and why nobody talks about it
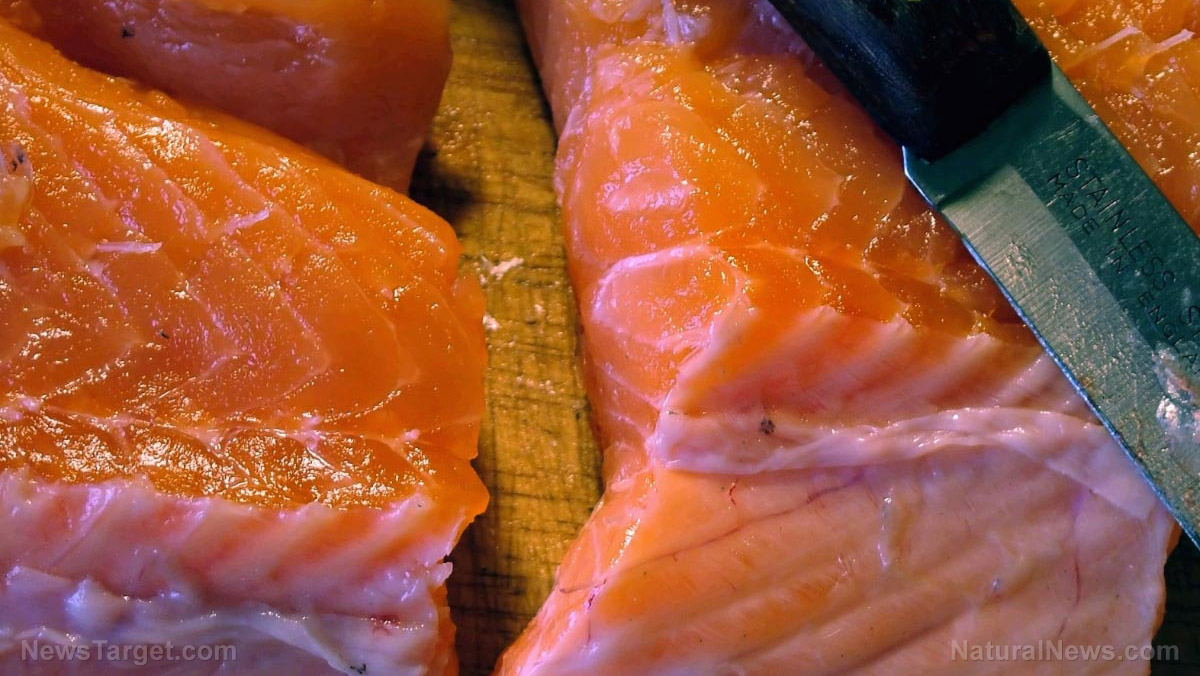
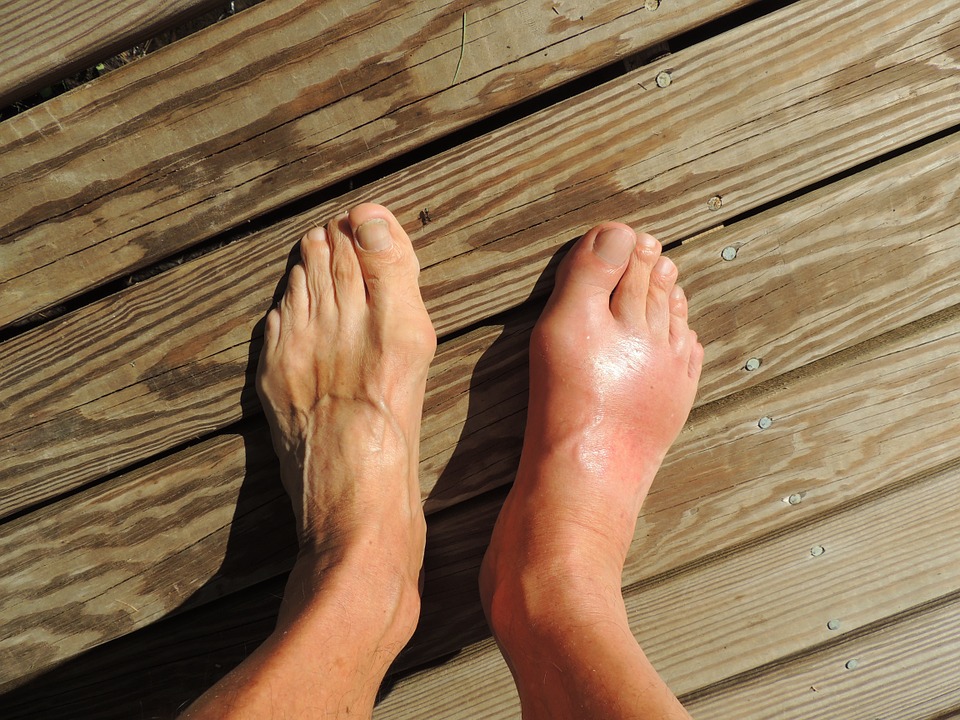
Gout refers to a form of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid in the joints, or hyperuricemia. When a person eats foods rich in purine, like beef and seafood, the body produces uric acid to break these down. However, when his uric acid levels become too high, this can cause uric acid crystals (monosodium urate) to form. They most commonly form in the joints of the big toe, but they can be seen in other joints like the fingers, elbows and ankles.
People who have gout experience sudden, intense pain in the area affected. The tissues surrounding the joint swell, turn red and become exceedingly tender to the touch. After a gout attack, a person’s movements become severely limited. It makes putting shoes, socks or even placing a blanket on it unbearable. Most people who have it limp or stay seated to deal with the pain.
Gout-shamed: A look into its history
Even though many people suffer from gout, not everyone seeks treatment. A recent poll showed that having gout invokes feelings of shame and embarrassment that holds them back from getting help. This is a problem because people who have gout are more vulnerable to developing heart disease and kidney stones.
This stigma stems from gout’s infamous reputation in history. Gout is commonly associated with the nobles and their excessively luxurious lifestyles – most famous of whom was King Henry VIII. In fact, gout was so common among them that it was dubbed the “disease of kings.” While people no longer think that gout is limited to nobles and kings, its association with an opulent lifestyle remains.
Does diet have anything to do with gout?
Consuming certain foods and drinks cause an increase in uric acid levels, which contribute to gout. This includes alcohol, sweetened beverages, meat and shellfish. Some people are also predisposed to gout. In a study published in BMJ, researchers even suggested that compared to genetic factors, diet has a significantly smaller contribution to the development of gout.
How to prevent gout
Regardless of its etiology, here are some ways to reduce its risk:
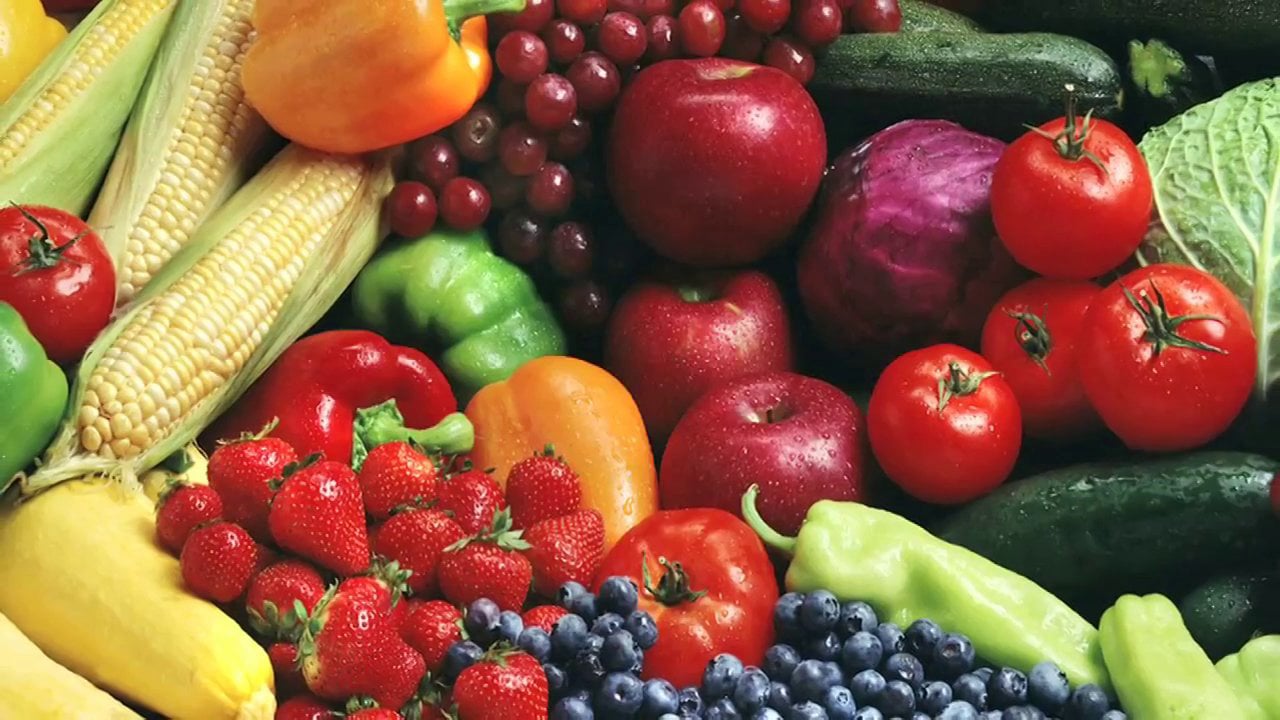
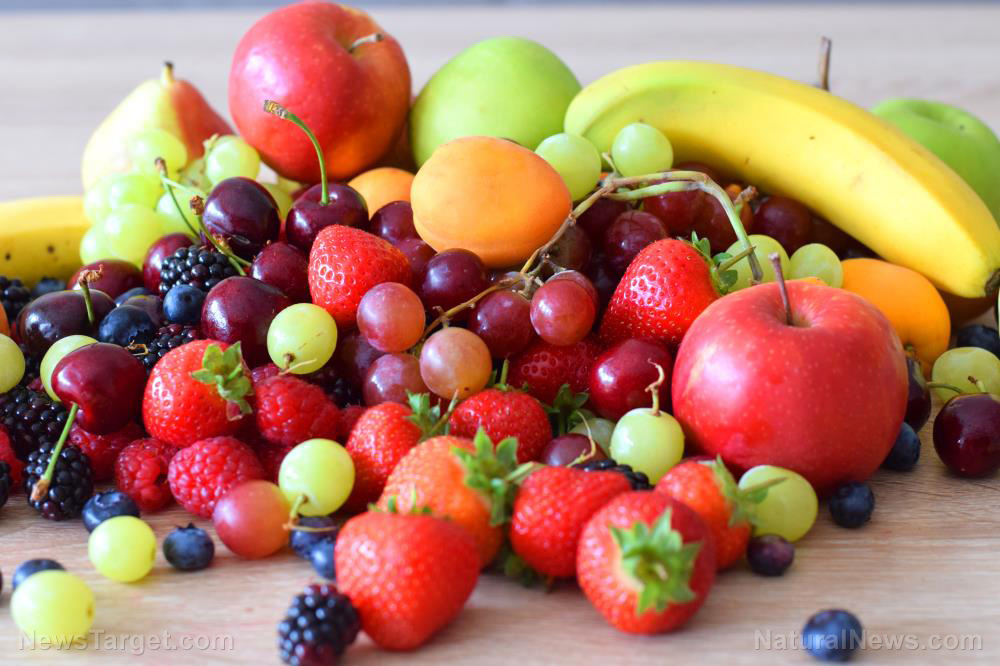
- Eat foods rich in vitamin C. This is a compound that helps reduce uric acid levels. Foods rich in vitamin C include lemons, spinach, and strawberries.
- Start adding cherries to daily meals. Eating cherries can significantly reduce uric acid levels and minimally reduce inflammation as well. They have been used as a popular home remedy for gout.
- Avoid foods rich in purines. Eating meat and seafood may contribute to the development of gout. Limiting the consumption of these foods may help fend it off.
Like any other health condition, gout may have been brought about by a series of bad eating habits. It is always best to seek help and treatment from healthcare professionals. (Related: Gout – Seek a drugless approach to this painful condition.)
Health.news has more stories on gout how to prevent it.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: ancient illnesses, beef, big toe, cherries, diet, disease of kings, gout, health shame, herbal remedies, hyperuricemia, inflammation, King Henry VIII, natural remedies, opulent lifestyle, pain relief, prevention, red swollen toe, seafood, uric acid, uric acid crystals, uric acid level
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
FoodIsMedicine.com is a fact-based public education website published by Food Is Medicine Features, LLC.
All content copyright © 2018 by Food Is Medicine Features, LLC.
Contact Us with Tips or Corrections
All trademarks, registered trademarks and servicemarks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.