Avoid sun damage with superfoods that offer photoprotective benefits for your skin
04/29/2022 / By Zoey Sky

More than five million people are treated for skin cancer every year, but the condition can be prevented with minimal intervention. And even though there are safe vitamin D synthesizing periods to spend in the sun, safe sun protection is essential for your skin health.
Instead of slathering on conventional sunscreens with harmful ingredients, it’s better to consume superfoods that can help boost your skin health and prevent sun damage.
Did you know that you can reap amazing photoprotection benefits by eating camu camu berries or using camu camu powder? You can also enjoy similar health benefits by taking microalgae like spirulina.
Avoid toxic sunscreens and look for natural alternatives
When talking about nanoparticle safety, remember that nanoparticles vary by shape, size and coating. This means their properties make it difficult for consumers to know which ones are safe. (Related: The unwanted side effects of sunscreen, and some natural alternatives.)
Unfortunately, consumers are often confused by the misleading labeling used by manufacturers. These labels make it hard to determine which sunscreens are safe to use and which may cause sun damage to the skin.
The International Agency for Research on Carcinogens labels titanium dioxide as a potential carcinogen. When either titanium dioxide or zinc oxide are inhaled, they cause direct harm to lung tissue.
Follow these safety tips when purchasing sunscreen:
- Look for uncoated zinc oxide or uncoated non-nano zinc oxide sunscreen.
- When buying sunscreen, look for products that only contain ingredients that will not be harmful if absorbed into the skin.
- Get sunscreen labeled as broad-spectrum and has at least an SPF of 30 so it can protect against both ultraviolet B (UVB) and ultraviolet A (UVA) rays.
- Limit yourself to only 20 minutes of direct sunlight daily without using topical sunscreen.
Boost your skin health with superfoods
Countless studies have proven the health benefits of vitamin C. According to research at the Linus Pauling Institute of Oregon State University, concentrations of vitamin C present in the dermis and epidermis may help prevent UV-induced photo-damage.
Topical applications can boost C levels in the skin and the stratum corneum or the outermost layer of your epidermis is a primary obstacle to absorption.
But researchers found that vitamin C preparations with low pH levels around 4, like the uncharged form of vitamin C or ascorbic acid, are more bioavailable and can be absorbed into the epidermal layer.
And while vitamin C offers skin-protective benefits, these are not direct. The skin health benefits of vitamin C are attributed to its antioxidant properties that offer protection against UV-induced, free-radical damage.
Data also suggests that combining vitamin C orally with vitamin E may mutually enhance the skin-protective properties of the two vitamins.
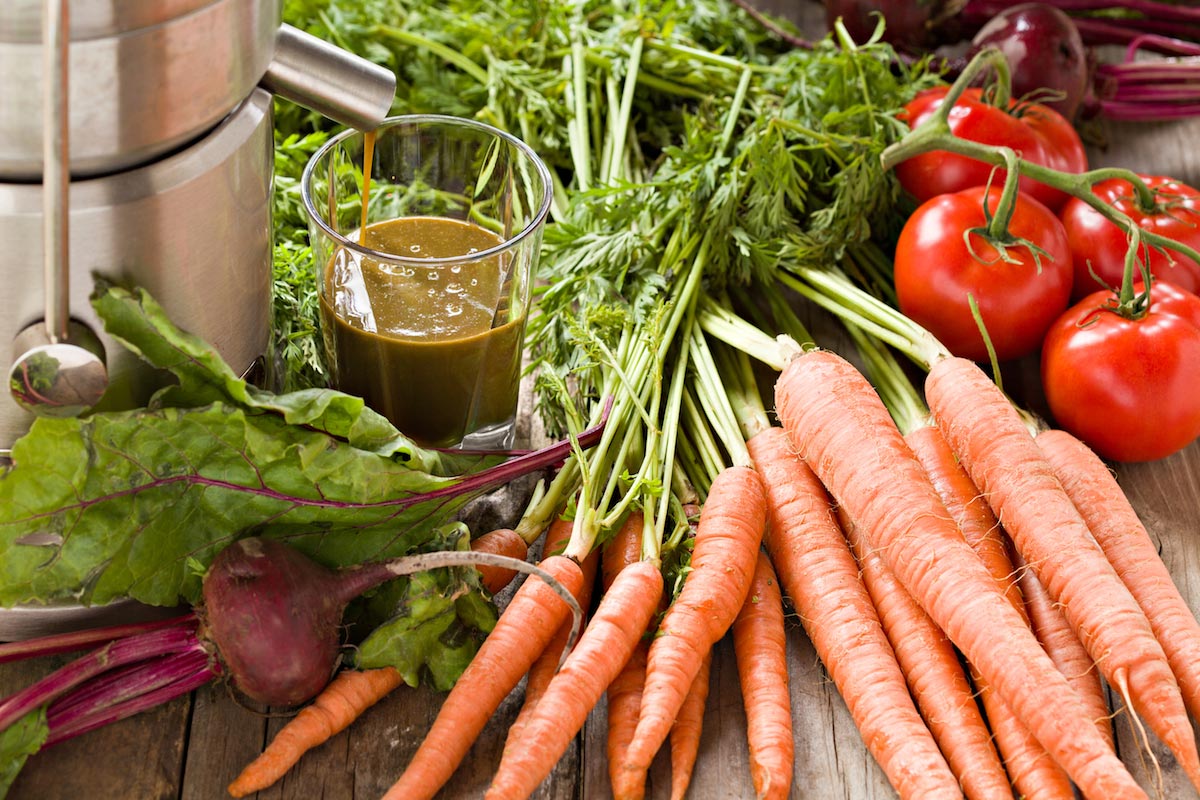
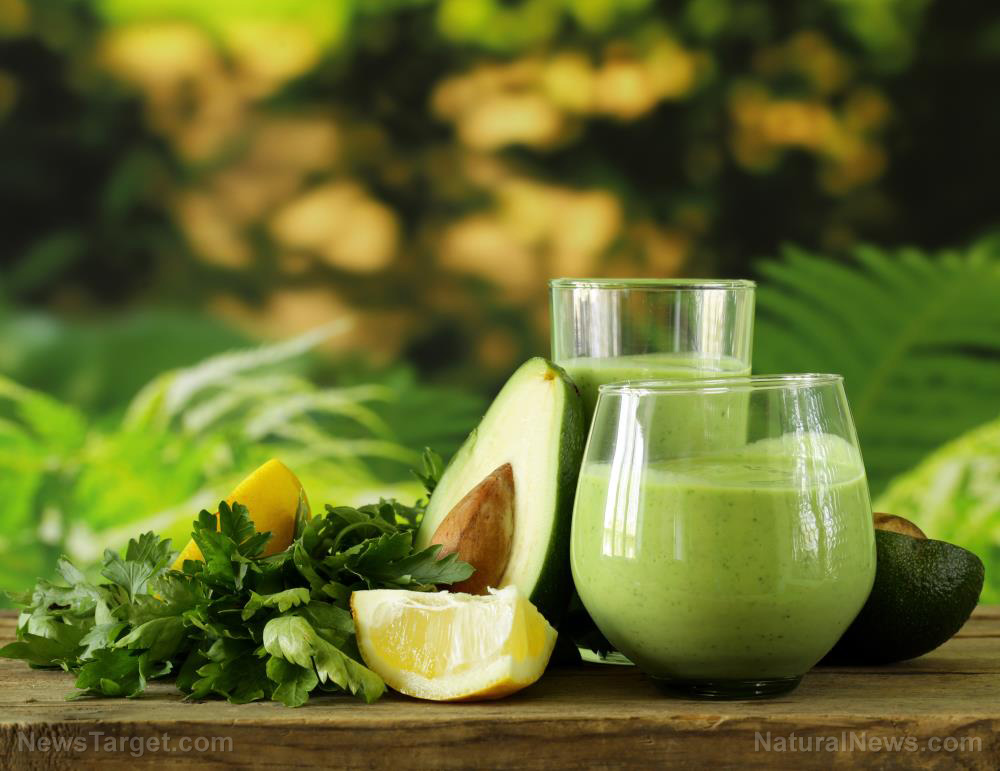
Consuming superfoods full of beneficial antioxidants can help protect you from the sun’s harmful UV rays. If you want a more efficient way of boosting your fruit and vegetable intake, try consuming green juices.
Below are some nutritious fruits and vegetables that you can consume more to protect yourself from the potential threats of sun exposure:
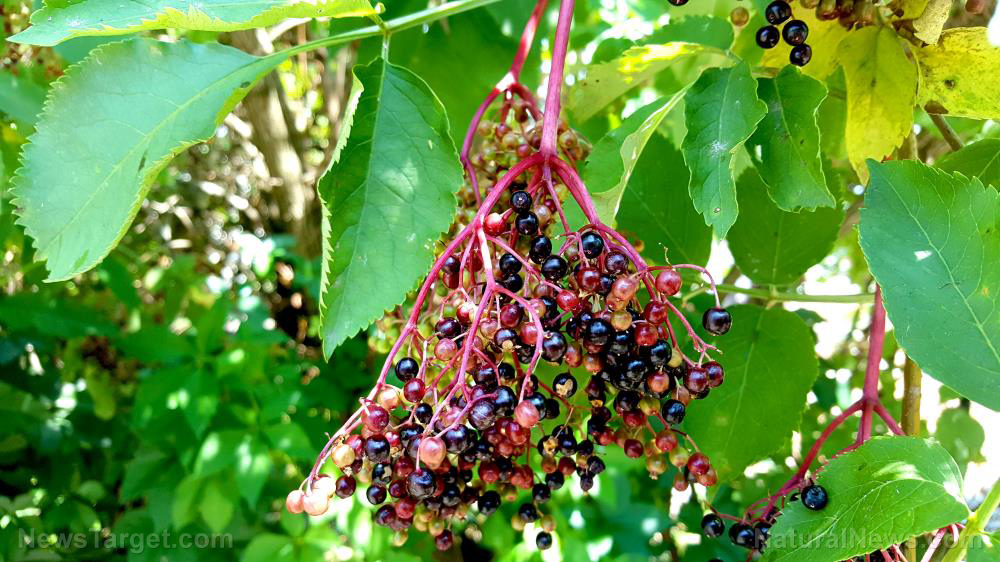
- Camu camu berry – Camu camu berry contains 50 times more vitamin C than oranges. Use camu camu berry powder and make some fruit smoothies or green juices to maximize its use.
- Microalgae – Microalgae like spirulina and blue-green algae contain astaxanthin. Astaxanthin can be used topically to promote healthy skin. According to a 2012 study, combining topical and oral doses of astaxanthin can help smoothen wrinkles, make age spots smaller and help maintain skin moisture.
When making fruit smoothies, green juices or various dishes, add superfoods like avocados, cacao, carrots, cinnamon and dark berries to naturally boost antioxidant activity.
Don’t put yourself at risk by using sunscreens with harmful chemicals. Instead of using conventional sunscreens, look for alternatives that contain non-toxic ingredients and boost your skin health by consuming sun-protecting superfoods like camu camu berry or spirulina.
Visit Superfoods.news for more information about foods that help boost skin health.
Watch the video below for more tips on how to avoid toxic sunscreen ingredients.
This video is from the Dr. Edward Group channel on Brighteon.com.
More related stories:
Eat these foods to protect the skin from sun damage.
Eating these 9 superfoods will help heal sun-damaged skin.
Botanical interventions for low-risk skin cancers.
These herbs can protect your skin from cancer, says research.
Another possible carcinogen found in popular sunscreen brands.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
aging secrets, alternative medicine, anti-aging, antioxidants, food is medicine, food science, functional food, natural health, natural medicine, nutrients, skin cancer, skin care, skin health, sun damage, vitamin C
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
FoodIsMedicine.com is a fact-based public education website published by Food Is Medicine Features, LLC.
All content copyright © 2018 by Food Is Medicine Features, LLC.
Contact Us with Tips or Corrections
All trademarks, registered trademarks and servicemarks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.